June 2016 Update: Times change fast! Already, the
migrate_source_jsonmodule mentioned in the post has been (mostly) merged directly into themigrate_plusmodule, so if you're building a new migration now, you should use themigrate_plusJSON plugin if at all possible. See Mike Ryan's blog post Drupal 8 plugins for XML and JSON migrations for more info.
Recently I needed to migrate a small set of content into a Drupal 8 site from a JSON feed, and since documentation for this particular scenario is slightly thin, I decided I'd post the entire process here.
I was given a JSON feed available over the public URL http://www.example.com/api/products.json which looked something like:
{
"upcs" : [ "11111", "22222" ],
"products" : [ {
"upc" : "11111",
"name" : "Widget",
"description" : "Helpful for many things.",
"price" : "14.99"
}, {
"upc" : "22222",
"name" : "Sprocket",
"description" : "Helpful for things needing sprockets.",
"price" : "8.99"
} ]
}I first created a new 'Product' content type inside Drupal, with the Title field label changed to 'Name', and with additional fields for UPC, Description, and Price. Then I needed to migrate all the data in the JSON feed into Drupal, in the product content type.
Note: at the time of this writing, Drupal 8.1.0 had just been released, and many of the migrate ecosystem of modules (still labeled experimental in Drupal core) require specific or dev versions to work correctly with Drupal 8.1.x's version of the Migrate module.
Required modules
Drupal core includes the base 'Migrate' module, but you'll need to download and enable all the following modules to create JSON migrations:
- Migrate (in core)
- Migrate Plus 8.x-2.x
- Migrate Tools 8.x-2.x
- Migrate Source JSON 8.x-1.x (currently, requires this patch for Drupal 8.1.x+ compatibility)
After enabling those modules, you should be able to use the standard Drush commands provided by Migrate Tools to view information about migrations (migrate-status), run a migration (migrate-import [migration]), rollback a migration (migrate-rollback [migration]), etc.
The next step is creating your own custom migration by adding custom migration configuration via a module:
Create a Custom Migration Module
In Drupal 8, instead of creating a special migration class for each migration, registering the migrations in an info hook, etc., you can just create a migration configuration YAML file inside config/install (or, technically, config/optional if you're including the migration config inside a module that does a bunch of other things and may or may not be used with the Migration module enabled), then when your module is installed, the migration configuration is read into the active configuration store.
The first step in creating a custom migration module in Drupal 8 is to create an folder (in this case, migrate_custom_product), and then create an info file with the module information, named migrate_custom_product.info.yml, with the following contents:
type: module
name: Migrate Custom Product
description: 'Custom product migration.'
package: Migration
core: 8.x
dependencies:
- migrate_plus
- migrate_source_jsonNext, we need to create a migration configuration file, so inside migrate_custom_product/config/install, add a file titled migrate_plus.migration.product.yml (I'm going to call the migration product to keep things simple). Inside this file, define the entire JSON migration (don't worry, I'll go through each part of this configuration in detail later!):
# Migration configuration for products.
id: product
label: Product
migration_group: Products
migration_dependencies: {}
source:
plugin: json_source
path: http://www.example.com/api/products.json
headers:
Accept: 'application/json'
identifier: upc
identifierDepth: 0
fields:
- upc
- name
- description
- price
destination:
plugin: entity:node
process:
type:
plugin: default_value
default_value: product
title: name
field_upc: upc
field_description: description
field_price: price
sticky:
plugin: default_value
default_value: 0
uid:
plugin: default_value
default_value: 0The first section defines the migration machine name (id), human-readable label, group, and dependencies. You don't need to separately define the group outside of the migration_group defined here, though you might want to if you have many related migrations that need the same general configuration (see the migrate_example module included in Migrate Plus for more).
source:
plugin: json_source
path: http://www.example.com/api/products.json
headers:
Accept: 'application/json'
identifier: upc
identifierDepth: 1
fields:
- upc
- title
- description
- priceThe source section defines the migration source and provides extra data to help the source plugin know what information to retrieve, how it's formatted, etc. In this case, it's a very simple feed, and we don't need to do any special transformation to the data, so we can just give a list of fields to bring across into the Drupal Product content type.
The most important parts here are the path (which tells the JSON source plugin where to go to get the data), the identifier (the unique ID that should be used to match content in Drupal to content in the feed), and the identifierDepth (the level in the feed's hierarchy where the identifier is located).
destination:
plugin: entity:nodeNext we tell Migrate the data should be saved to a node entity (you could also define a destination of entity:taxonomy, entity:user, etc.).
process:
type:
plugin: default_value
default_value: product
title: name
field_upc: upc
field_description: description
field_price: price
sticky:
plugin: default_value
default_value: 0
uid:
plugin: default_value
default_value: 0Inside the process configuration, we'll tell Migrate which specific node type to migrate content into (in this case, product), then we'll give a simple field mapping between the Drupal field name (e.g. title) and the name of the field in the JSON feed's individual record (name). For certain properties, like a node's sticky status, or the uid, you can provide a default using the default_value plugin.
Enabling the module, running a migration
Once the module is ready, go to the module page or use Drush to enable it, then use migrate-status to make sure the Product migration configuration was picked up by Migrate:
$ drush migrate-status
Group: Products Status Total Imported Unprocessed Last imported
product Idle 2 0 2Use migrate-import to kick off the product migration:
$ drush migrate-import product
Processed 2 items (2 created, 0 updated, 0 failed, 0 ignored) - done with 'product' [status]You can then check under the content administration page to see if the products were migrated successfully:
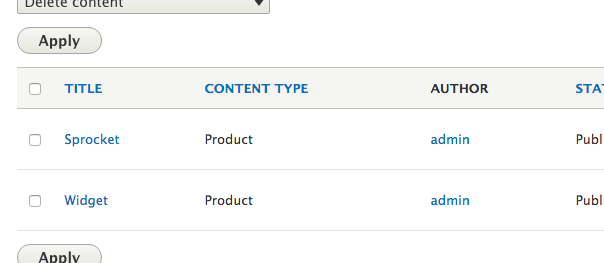
If the products appear here, you're done! But you'll probably need to do some extra data transformation using a custom JSONReader to transform the data from the JSON feed into your custom content type. That's another topic for another day! You can also update all the migrated products with migrate-import --update product, or rollback the migration with migrate-rollback product.
Note: Currently, the Migrate UI at
/admin/structure/migrateis broken in Drupal 8.1.x, so using Drush is the only way to inspect and interact with migrations; even with a working UI, it's generally best to use Drush to inspect, run, roll back, and otherwise interact with migrations.
Reinstalling the configuration for testing
Since the configuration you define inside your module's config/install directory is only read into the active configuration store at the time when you enable the module, you will need to re-import this configuration frequently while developing the migration. There are two ways you can do this. You could use some code like the following in your custom product migration's migrate_custom_product.install file:
<?php/** * Implements hook_uninstall(). */function migrate_custom_product_uninstall() { db_query("DELETE FROM {config} WHERE name LIKE 'migrate.migration.custom_product%'"); drupal_flush_all_caches();}?>...or you can use the Configuration Development module to easily re-import the configuration continuously or on-demand. The latter option is recommended, and is also the most efficient when dealing with more than just a single migration's configuration. I have a feeling config_devel will be a common module in a Drupal 8 developer's tool belt.
Diving Deeper
Some of the inspiration for this post was found in this more fully-featured example JSON migration module, which was referenced in the issue Include JSON example in the module on Drupal.org. You should also make sure to read through the Migrate API in Drupal 8 documentation.
Download the source code of the custom product migration module example used in this blog post.
Comments
Hi, first of all thank you for this post, it's very hard to find how to import a json feed in drupal8. I have copied your example and I modified the yml file about “identifierDepth” with 1 as value.
A question about mapping: if I have a nested structure in my json file like this http://www.webapp.usi.ch/persons.json – how can I get the internal phone in yml file?
My "fields":
My mapping:
Thank you in advance for your help.
It seems that it's not possible with the plain migrate_source_json, check the links at the "Diving deeper" part of the post. Basically you need to map them in code yourself. JSONpath support would be great, but not sure when that would be happening...
(Apologies as it seems a follow-up message was caught by the spam filter; this is from mErilainen:)
Actually, it's really easy:
field_name_internal_phone: phones/internal* Implements hook_uninstall().
*/
function migrate_custom_product_uninstall() {
db_query("DELETE FROM {config} WHERE name LIKE 'migrate.migration.custom_product%'");
drupal_flush_all_caches();
}
?>
Isn't it DELETE FROM {config} WHERE name LIKE 'migrate_plus.migration.custom_product% ???
Thank you to the Anonymous user who posted this a month ago -- you have saved me hours of stress. My migration was not showing up in the "migrate-status" until I renamed all my files from 'migrate.migration.foobar' to 'migrate_plus.migration.foobar' -- it is not at all clear to me why this might be the case, and why so many existing tutorials have the incorrect information. Thank you again.
A few people have asked how to make a dynamically configurable migration source URL (and I needed to do this a couple times in my own projects), so I'm posting some example code from a recent project here.
First, here's an example form (e.g.
example_migrate/src/Form/MigrationConfigurationForm.php) that allows the setting of a URL from within the site's admin UI:The migration itself is configured on install to not have a URL set, but once I install the
example_migratemodule, then save this form with the right URL, when I export the site's configuration, I have something like:id: examplelabel: 'Example nodes'
source:
plugin: url
track_changes: true
data_fetcher_plugin: http
data_parser_plugin: json
...
urls: 'http://www.example.com/endpoint'
...
Hi Jeff,
I am trying to import content (other Drupal 8 JSON content created by view).
https://jsfiddle.net/7fg7jgfk/
Here you can find my migrate_plus.migration.faq.yml in HTML section and my JSON file in JavaScript section.
After enabling my module, migrate-status can properly check the count of nodes to import, that's ok.
I'm trying to import FAQ content type nodes to the same content type on cloned site where the nodes are deleted.
However I can not import the node (I was trying to import a node with title only for start) because of this:
SQLSTATE[23000]: Integrity constraint violation: 1048 Column 'title' cannot be null: INSERT INTO [error]
{node_field_data} (nid, vid, type, langcode, title, uid, status, created, changed, promote, sticky, revision_translation_affected, default_langcode) VALUES...
I think that this part is a problem:
process:
type:
plugin: default_value
default_value: faq
title: title/value
What should be the right mapping for these fields?
Best,
Greg
Thanks Jeff for the great write up.
I'm trying to get something very similar to this working using just migrate_plus (since migrate_source_json has been deprecated). I keep running an error when trying to use
plugin: url
data_fetcher_plugin: http
data_parser_plugin: json
per the advanced json example.
Error message: cURL error 6: Could not resolve host: http (see http://curl.haxx.se/libcurl/c/libcurl-errors.html) at .
I get this regardless as to what source URL I use.
What modifications would need to be made to migrate_plus.migration.product.yml to use just migration_plus without the now deprecated module?
Thanks again!!
Shawn
I am following this blog post and when I run the drush ms command I get this error.
"Passed variable is not an array or object, using empty array instead"
As far as I can tell I have follow all the steps in the post correctly. This is homework in preparation for a bigger more complex JSON import into Drupal 8.
Nevermind got it sorted
I'm really having a hard time with the file/folder structure.
root/modules/migrate_custom_product
root/modules/migrate_custom_product/migrate_custom_product.info.yml
root/modules/migrate_custom_product/config/
root/modules/migrate_custom_product/config/install/
root/modules/migrate_custom_product/config/install/migrate_plus.migration.product.yml
This is the structure I am now having. Is this okay?
When I run drush migrate-status, it outputs ' Group: Default' and not 'Products'
I am trying to migrate json file following the steps you gave but I am continuously getting an error:-
[error] No migrations found.
Can anyone help me with this please.